Theory
Alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. The alternating current is a current that flows through power lines and the electricity normally available at home that flows from wall sockets. The standard current used in the USA is 60 cycles per second - frequency of 60 Hz; in Europe and in most of the world it is 50 cycles per second - frequency of 50 Hz.
Direct current (DC) is the electrical current that flows constantly in one direction. For instance, the type of current that flows in a lamp or in any other device that uses batteries is direct current.
The purpose of a direct current generator is to artificially and permanently maintain a voltage drop in the circuit. Batteries, accumulators, dynamos, alternators and photo batteries or photovoltaic cells are generators.
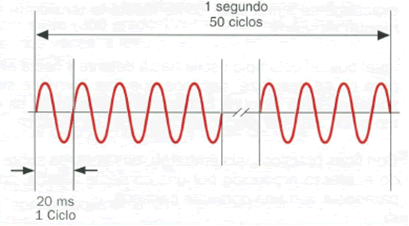
Alternating Current
An alternating signal changes over time and has a frequency, period.
- Resistors (R) do not understand either time or frequencies.
- The capacitors (C) and the inductance (L) work on frequency.
AC generators (alternators) are more effective and simple than DC ones (dynamos). They are important for many reasons:
a) Almost all electrical energy that is generated in world for industry and domestic use is this type. There are numerous energy receivers that can be used.
b) The current at such systems can be analysed as a superposition of sinusoidal currents with different frequencies (Fourier analysis). Moreover, converting AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) is not a complicated procedure.