Alternating signal generators
An AC generator operates by rotating a wire coil within a magnetic field with constant angular speed, ω. It produces electromotive force (emf) that alternate over time in sinusoidal form as follows:
V(t) =Vm senω t
In which Vm is the maximum voltage or peak value (see following figure) and ω = 2π f is the angular frequency, with f being the frequency expressed in Hertz.
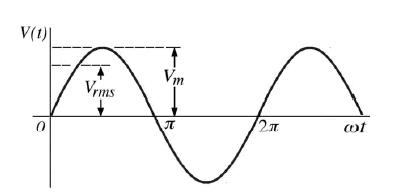
Representation of voltage according to time
On Figure above the concept of effective value or rms (root-mean-square) appears. We are able to detect that for sinusoidal signals rms equals the maximum value divided by the square root of 2:
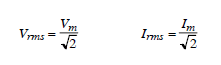
In case of voltage specifications for an alternating source, we always refer to the effective voltage or rms. Thus, when we say that the voltage of the home network is 110 volts, this corresponds to a peak voltage of 110 V multiplied by the square root of 2, i.e. 156 V.
On the other hand alternating current voltmeters and ammeters measure effective values.