Series Parallel Circuits
A series-parallel circuit has some
components in series and others in parallel. The power source and control or
protection devices are usually in series; the loads are usually in parallel.
The same current flows in the series portion, different currents in the
parallel portion. The same voltage is applied to parallel devices, different
voltages to series devices. If the series portion is broken, current stops
flowing in the entire circuit. If a parallel branch is broken, current
continues flowing in the series portion and the remaining branches.
A resistance and lamps may be
connected in a circuit as illustrated below. This type of connecting method is
called series-parallel connection, and is a combination of series and parallel
connections. The interior dash board lights are a good example. By adjusting
the rheostat, you can increase or decrease the brilliance of the lights.
Serial and parallel circuit
a.
practical view; b. electronical view
The
switch has the role to provide current to the circuit so that the other
components can function properly. And the power supply has the principal role
to generate energy for the circuit.
The
combined resistance R02 in this series-parallel connection can be
determined in the following order:
·
determine
combined resistance R01, which is a combination of resistances R2
and R3 connected in parallel;
· then, determine resistance R02, which is a combination of resistance R1 and combined resistance R01 connected in series.

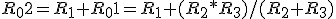
Total current I flowing in the circuit can be determined from Ohm's law as follows:

The
voltage applied to R2 and R3 can be found by the
following formula:
