Remote Labs with Data Acquisition (DAQ) Cards
Remote laboratories based on data acquisition
cards offer a more versatile solution, as a great part of the lab equipment’s
can be replaced by a single DAQ card.
For remote laboratories involving exercises
with analog circuits, for example, we are likely to have virtual instruments
programmed to perform the tasks of a function generator and oscilloscope. These
instruments are created by using virtual instrumentation and are programmed to
use the resources of a DAQ card to generate analog waveforms and to read analog
signals. User interfaces can be created to look similar to real devices and
therefore can add the atmosphere and feeling of a real environment.
In order to create a remote laboratory with a
DAQ card it is necessary to previously consider the types of exercises to be
performed, so that the proper DAQ device can be chosen. Experiments can vary on
the required signal frequencies and this must be taken into account if we want
the circuit behavior to be well visualized.
In the field of electronics, one example of a
remote laboratory implemented using a data acquisition card is provided by the
Carinthia University of Applied Sciences. This is a hybrid online lab and
consists of a programmable analog ASIC device (ispPAC 10) that implements a
variety of common analog functions. The circuit can be programmed and tested
remotely.
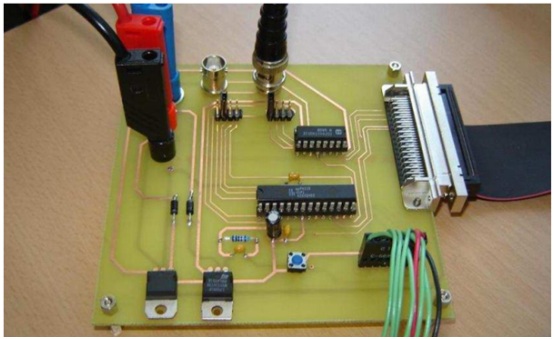
Figure 6 shows the PCB (Print Circuit board)
assembled for this remote lab. The DAQ hardware used with this lab was the
PCI-6251 from National Instruments is a high-speed multifunction data
acquisition (DAQ) board (for more details regarding technical characteristics
of this board visit).
This device has 16 analog inputs and 2 analog outputs. The data acquisition
terminals were connected to the proper inputs and outputs of the ASIC in order
that the signal on each I/O terminal could be acquired and displayed to the
user. The server that controls the hardware of the ASIC remote laboratory runs
LabVIEW and it’s built in Web server, which publishes the virtual
instruments.
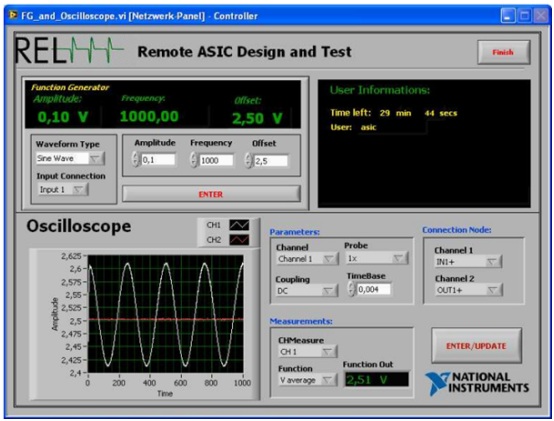
The DAQ hardware for this lab was programmed to
acquire a finite number of samples and the sampling rate is adjusted according
to the time interval specified by the user. Remote Laboratories based on
Embedded Web Servers
Today, very compact Embedded Web servers (Micro
Web servers, MWS) can be used in a wide range of applications. It can replace
personal computers required in remote labs with special hard- and software.
They can be used in educational and also in industrial environments. MWS are
cheap, and almost every measuring instrument has a serial port (which is used
for the connection to the MWS). Up to seven instruments can be connected to one
MWS at the same time. Measurement results can also be transferred to computers
running software like MatLab,
Simulink etc., to carry out further numerical and graphical analysis.
Figure 9 shows a typical configuration of hardware control using Micro Web server technology.
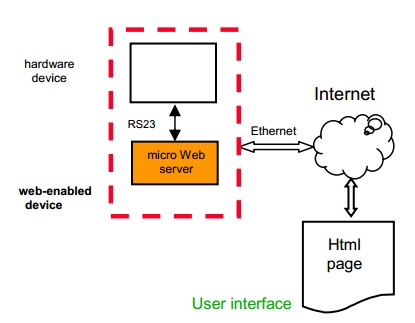
Micro Web servers make the executions of
different user interfaces (UI) possible, html pages or flash animations are
especially suited. This equipment allows getting a feeling that users are
controlling a real instrument panel by using e.g. a touch screen (Figure 10).
