Radiation
Radiation is the mode of
heat transfer which refers to transmitted energy of a surface in its
surroundings. A heated surface of finite temperature, which interacts with a
medium of a different temperature, emits energy in the form of electromagnetic
waves.
Thermal radiation is the
energy generated by a matter that is at a higher finite temperature. In the
radiation process, the transfer of energy occurs most efficiently in a vacuum
and does not necessarily requires the presence of a material medium like in the
conduction and convection processes.
For a better understanding
of the thermal radiation process, further we will focus on the emission from
the solid surfaces.
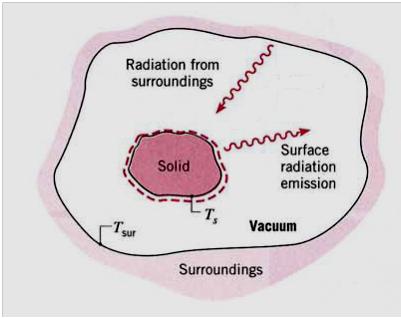
The radiation process of a solid surface [10] is shown in Figure1. After heating of a solid to a higher temperature (Ts), its surface emits radiation its surroundings. This emitted radiation is called the emissive power (E) and comes from the internal energy of the matter and the rate at which the energy is emitted by matter per unit area (W/m2). The solid is cooling until it will achieve the surrounding temperature (Tsur) this means that the solid will be in thermal equilibrium with its surroundings.